Specialist immunisation services
Lý lịch
Specialist immunisation services (SIS) are hospital-based immunisation clinics led by a team of specialised medical and nursing staff with expertise in vaccines and immunisation.
In Victoria, there are specialised immunisation services at Monash Health, Western Health, Royal Children’s Hospital and Alfred Health.
Purpose of SIS
These services offer vaccination encounters through walk-ins, or via formal appointments for patients with more complex vaccination needs (e.g. multiple medical conditions, antenatal vaccination, complex catch-up plans, oncology, pre- and post-transplant recipients).
SIS in Victoria are also linked with SAEFVIC, the Victorian vaccine safety service. Specialist consultation and/or vaccination under supervision may be facilitated via these services for individuals who have previously experienced a significant adverse event following immunisation (AEFI) or who are at higher risk of experiencing an AEFI.
Access and services offered
Dịch vụ Chủng ngừa của Bệnh viện Nhi đồng Hoàng gia
Suited for:
Children of all ages and family members (*BCG appointments only available for children < 12 months of age)Services offered:
NIP and travel vaccines, catch-up vaccination (appointments required), COVID-19 vaccines (from 6 months of age), meningococcal B/ACWY, sedation services and complex vaccination needsHours of operation:
Monday to Friday 9:00 am–4:30 pm, excluding public holidaysHow to access:
Walk-ins and appointments availableHow to refer:
Immunisation clinic fax number: (03) 9345 4163
BCG clinic fax number: (03) 9345 5034
Inpatients/outpatients (seen by Immunisation Nurse Practitioners) fax number: (03) 9345 4100Vị trí:
Ground floor opposite Parkville Café, Royal Children’s Hospital, ParkvilleContact:
Telephone: 1300 882 924 (option 2) or (03) 9345 6599 / 9345 6399
E-mail: [email protected]Monash Immunisation Service
Suited for:
All ages (*BCG appointments only available for children < 5 years of age)Services offered:
National Immunisation Program (NIP) and travel vaccines, catch-up plans and vaccination, sedation services, complex vaccination needs Và COVID-19 vaccines (≥ 6 months)Hours of operation:
Monday to Friday 8:30 am–4:00 pm, excluding public holidays.How to access:
Walk-ins and appointmentsVị trí:
Suite I, Jessie McPherson Private Consulting Suite Level 2, Monash Medical Centre, ClaytonHow to refer:
Monash Health require all referrals to be submitted from your GP via HealthLink: Monash Health referralsContact:
Telephone: (03) 9594 6320
E-mail: tiêm chủ[email protected]Western Health Immunisation Service
Suited for:
Children and pregnant peopleServices offered:
NIP vaccines (children), antenatal vaccines (dTpa Và cúm) and COVID-19 vaccines (≥ 6 months)Hours of operation:
Monday to Friday 9:00 am–4:00 pm, excluding public holidaysHow to access:
Walk-ins and appointments (appointments held on Wednesday afternoons only)Vị trí:
Ground Floor, Sunshine Hospital, Joan Kirner Women and Children’s Hospital, St AlbansHow to refer:
Western Health require all external patients to be referral through the general paediatric referral system: Western Health ReferralContact:
Telephone: (03) 8345 1727
E-mail: [email protected]Alfred Health Specialist Immunisation Services (AHSIS)
Suited for:
Adults only (≥ 18 years)Services offered:
Individuals who have experienced AEFI or who are at risk of experiencing AEFIHow to access:
By appointment onlyHow to refer:
Referrals can be made to Alfred Health Specialist Clinics and sent via Fax: (03) 90766938 or Email: [email protected]Contact:
Telephone: (03) 90765200
Kinh phí
The Royal Children’s Hospital, Monash and Western Health services operate with funding from the Victorian Department of Health. Alfred Health Specialist Immunisation Service is fully funded internally by Alfred Health.
Tài liệu
- MVEC: SAEFVIC
- MVEC: Chứng sợ kim tiêm
- MVEC: Viêm não mô cầu
- MVEC: Asplenia và hyposplenia
- MVEC: Cancer immunisation guideline
- MVEC: Solid organ transplant
- MVEC: BCG/Tuberculosis
- MVEC: Cúm
Các tác giả: Adele Harris (Immunisation nurse, SAEFVIC, Murdoch Children’s Research Institute) and Rachael McGuire (MVEC Education Nurse Coordinator)
Ngày: tháng 3 năm 2024
Tài liệu trong phần này được cập nhật khi có thông tin mới và có vắc-xin. Nhân viên của Trung Tâm Giáo Dục Vắc-xin Melbourne (MVEC) thường xuyên xem xét độ chính xác của các tài liệu.
You should not consider the information on this site to be specific, professional medical advice for your personal health or for your family’s personal health. For medical concerns, including decisions about vaccinations, medications and other treatments, you should always consult a healthcare professional.
Giám sát các sự kiện bất lợi sau khi tiêm chủng trong cộng đồng (SAEFVIC)
SAEFVIC (Surveillance of Adverse Events Following Vaccination In the Community) is the central reporting service in Victoria for any significant adverse event following immunisation (AEFI).
An AEFI is defined by the Australian Immunisation Handbook as “any untoward medical occurrence that follows immunisation. It does not necessarily have a causal relationship with the vaccine”. A vaccine error is also considered an AEFI and may be related to the way a vaccine was stored, prepared or administered.
Reporting adverse events is not mandatory in Victoria, however doing so allows the rapid investigation of any potential vaccine or system problems by Victorian and national health authorities (Therapeutic Goods Administration). This helps to ensure a safe and effective immunisation program and it maintains community confidence in vaccines.
Sau báo cáo về các tác dụng phụ, SAEFVIC có thể tạo điều kiện hỗ trợ lâm sàng cá nhân hóa cho bệnh nhân và gia đình bị ảnh hưởng bởi AEFI. Điều này có thể được thực hiện thông qua tư vấn trực tiếp hoặc chăm sóc sức khỏe từ xa với bác sĩ chuyên khoa hoặc với y tá tiêm chủng qua điện thoại.
Vui lòng gặp bác sĩ gia đình, khoa cấp cứu địa phương hoặc gọi 000 nếu cần hỗ trợ ngay lập tức.
Tài liệu
- SAEFVIC
- MVEC: Dịch vụ Chủng ngừa Chuyên gia Victoria (VicSIS)
- MVEC: Báo cáo các biến cố bất lợi tại Úc
- MVEC: AusVaxSafety: giám sát an toàn vắc-xin tại Úc
Các tác giả: Nigel Crawford (Giám đốc, SAEFVIC, Viện nghiên cứu trẻ em Murdoch), Georgina Lewis (Giám đốc lâm sàng, SAEFVIC, Viện nghiên cứu trẻ em Murdoch) và Rachael McGuire (Y tá nghiên cứu, SAEFVIC, Viện nghiên cứu trẻ em Murdoch)
Được xem xét bởi: Rachael McGuire (Điều Phối Viên Y Tá Giáo Dục MVEC)
Ngày: Tháng Mười 20, 2022
Tài liệu trong phần này được cập nhật khi có thông tin mới và có vắc-xin. Nhân viên của Trung Tâm Giáo Dục Vắc-xin Melbourne (MVEC) thường xuyên xem xét độ chính xác của các tài liệu.
Quý vị không nên coi thông tin trong trang web này là tư vấn y tế chuyên nghiệp, cụ thể cho sức khỏe cá nhân của quý vị hay của gia đình quý vị. Đối với các lo ngại về y tế, bao gồm các quyết định về chủng ngừa, thuốc men và các phương pháp điều trị khác, quý vị luôn phải tham khảo ý kiến của chuyên viên chăm sóc sức khỏe.
Chấn thương vai liên quan đến tiêm vắc-xin (SIRVA)
Cúm là gì?
Shoulder Injury Related to Vaccine Administration (SIRVA) is a rare but serious complication following suspected inadvertent administration of a vaccine too high in the deltoid or into the shoulder joint. This may cause a local inflammatory response and potential trauma to local structures within the shoulder joint including bursae, ligaments and tendons resulting in sudden onset shoulder pain and restricted movement. Symptoms can last for weeks to months or as long as years. Affected individuals can experience varying degrees of disability which can impact on their activities of daily living, social and emotional wellbeing.
Symptoms
Distinguishing symptoms/features of SIRVA include:
- sudden onset shoulder pain within 48 hours of vaccination- different to the injection site pain expected following vaccination
- restricted range of movement (RROM) of affected shoulder
- persistent shoulder pain and RROM lasting >1 week, lasting weeks to months
- suspicion of incorrect vaccination site – too high in the upper arm.
Impacts and implications
The impacts of SIRVA can include:
- interrupted sleep due to pain
- difficulty with personal care, care of others and activities of daily living
- inability to participate in sports or hobbies
- tôiodified work duties
- time off work related to symptoms and/or treatments and investigations
- tôioss of income due to time off work
- financial burden due to cost of treatments and investigations
- emotional and social wellbeing.
Further implications for an individual with SIRVA can include vaccine hesitancy, reduced confidence in healthcare/immunisation providers and the potential for impaired immunogenicity.
Diagnosis
A GP, specialist or allied health professional such as a physiotherapist can diagnose SIRVA based on presenting symptoms and clinical history following an immunisation.
If radiological investigations such as ultrasound or MRI are undertaken to support or confirm a diagnosis, abnormalities including bursitis, adhesive capsulitis, impingement syndrome, synovitis or tendon tears may be identified.
Early diagnosis of SIRVA leads to timely treatment which is thought to lessen the duration and severity of symptoms.
Treatment options
SIRVA can be treated in a variety of ways and may include any of the following:
- over the counter pain/anti-inflammatory medications
- prescription pain/anti-inflammatory medication
- oral corticosteroids
- corticosteroid joint injections
- physiotherapy or other allied health professionals
- massage
- surgery(rare).
How to prevent SIRVA
SIRVA can be prevented by following the recommended vaccination procedureS for correct injection technique.
| Expose | Identify | Imagine | Inject |
| Expose the whole upper arm | Identify upper and lower anatomical landmarks (acromion and deltoid tuberosity) | Imagine an inverted triangle 2-3 fingers below the acromion | Inject vaccine in the centre of the triangle into the deltoid muscle |
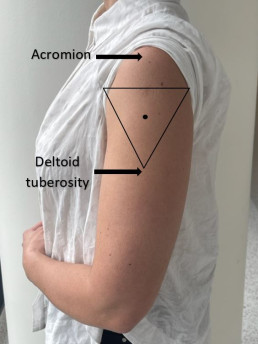
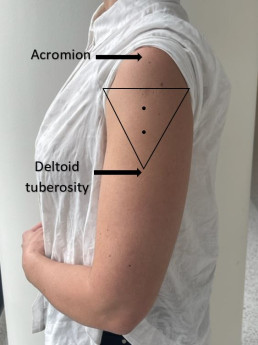
Vui lòng tham khảo trước MVEC: Quản lý tiêm vắc xin- đúng kỹ thuật for further information on correct injection technique.
Where to report a case of SIRVA
All confirmed or suspected cases of SIRVA should be reported to SAEFVIC (the Victorian vaccine safety service). Reports can be made by consumers, immunisation providers or treating healthcare professionals.
SAEFVIC can provide clinical advice or facilitate consultation with an immunisation specialist if required.
Tài liệu
- MVEC: Quản lý tiêm vắc xin- đúng kỹ thuật
- MVEC Education portal eLearning package: Shoulder Injury Related to Vaccine Administration (SIRVA)
- Australian immunisation handbook: Avoiding shoulder injury related to vaccine administration
- SIRVA (Shoulder injury related to vaccine administration); A case series- “Are you on target?”
- Cross GB, Moghaddas J, Buttery J, Ayoub S, Korman TM. Don’t aim too high: Avoiding shoulder injury related to vaccine administration. Aust Fam Physician 2016;45(5):303-306
- Petrakis N, Addison M, Penak B, Schrader S, Mallard J, Clothier H. J , Buttery J. P, Crawford N. W & Cheng D. R (2023) Shoulder injury following COVID-19 vaccine administration: a case series and proposed diagnostic algorithm, Expert Review of Vaccines, 22:1, 299-306
Các tác giả: Mel Addison (SAEFVIC Research Nurse, Murdoch Children’s Research Institute), Rachael McGuire (SAEFVIC Research Nurse, Murdoch Children’s Research Institute), Georgie Lewis (SAEFVIC Clinical Manager, Murdoch Children’s Research Institute) and Nigel Crawford (Director SAEFVIC, Murdoch Children’s Research Institute)
Đượcxem xét bởi: Mel Addison (Y tá Nghiên cứu SAEFVIC, Viện Nghiên cứu Trẻ em Murdoch)
Ngày: Tháng Ba 23, 2023
Tài liệu trong phần này được cập nhật khi có thông tin mới và có vắc-xin. Nhân viên của Trung Tâm Giáo Dục Vắc-xin Melbourne (MVEC) thường xuyên xem xét độ chính xác của các tài liệu.
Quý vị không nên coi thông tin trong trang web này là tư vấn y tế chuyên nghiệp, cụ thể cho sức khỏe cá nhân của quý vị hay của gia đình quý vị. Đối với các lo ngại về y tế, bao gồm các quyết định về chủng ngừa, thuốc men và các phương pháp điều trị khác, quý vị luôn phải tham khảo ý kiến của chuyên viên chăm sóc sức khỏe.
Chương Rủi ro Đặc biệt trong Sổ tay Chủng ngừa Úc
Cúm là gì?
Những người có nguy cơ cao mắc các bệnh có thể phòng ngừa bằng vắc-xin (VPD) được xếp vào nhóm 'nguy cơ đặc biệt' trong Sổ tay Chủng ngừa Úc.
Điều này bao gồm các quần thể có nguy cơ đặc biệt (ví dụ: Thổ dân và Người đảo Torres Straight) và những người có nhu cầu tiêm vắc-xin bổ sung (ví dụ: tiêm phòng cho bà mẹ; trẻ sinh non). Nó cũng có các phần chi tiết về những người có nguy cơ đặc biệt do ức chế miễn dịch (bệnh và/hoặc điều trị), ví dụ như Asplenia, ung thư/hóa trị.
Chương này được cập nhật trực tuyến bằng các bằng chứng khoa học mới nhất hiện có
Sổ tay được xác nhận bởi:
- Nhóm tư vấn kỹ thuật về tiêm chủng Úc [ATAGI] và
- Hội đồng nghiên cứu y tế và sức khỏe quốc gia [NHMRC]
Tài liệu
- Cẩm nang Tiêm chủng Úc: Tiêm chủng cho các Nhóm Nguy cơ Đặc biệt
- MVEC: Nhóm tư vấn kỹ thuật của Úc về tiêm chủng
Đượcxem xét bởi: Nigel Crawford (Giám đốc, SAEFVIC, Viện Nghiên cứu Trẻ em Murdoch)
Ngày: tháng 9 năm 2018
Tài liệu trong phần này được cập nhật khi có thông tin mới và có vắc-xin. Nhân viên của Trung Tâm Giáo Dục Vắc-xin Melbourne (MVEC) thường xuyên xem xét độ chính xác của các tài liệu.
Quý vị không nên coi thông tin trong trang web này là tư vấn y tế chuyên nghiệp, cụ thể cho sức khỏe cá nhân của quý vị hay của gia đình quý vị. Đối với các lo ngại về y tế, bao gồm các quyết định về chủng ngừa, thuốc men và các phương pháp điều trị khác, quý vị luôn phải tham khảo ý kiến của chuyên viên chăm sóc sức khỏe.
Người nhận ghép tạng rắn: khuyến nghị tiêm chủng trước ghép
Lý lịch
In order to prevent the rejection of transplanted organs, people who have undergone a solid organ transplant require varying doses of immune suppressive medication. Once a patient is immune suppressed, seroprotection gained from immunisation may be suboptimal and therefore additional doses of vaccines may be recommended. Some vaccines (live-attenuated vaccines) may be contraindicated.
To overcome this and maximise immune responses it is recommended where possible that all vaccines are administered well before transplant with live-attenuated vaccines administered a minimum of 4 weeks prior to transplant.
Vui lòng tham khảo trước MVEC: Pre-solid organ transplant recipient immunisation guideline (0-18 years) để biết thêm thông tin.
For immunisation recommendations following a solid organ transplant please refer to your immunisation specialist for specific advice.
MVEC special risk guidelines
These guidelines have been prepared by immunisation staff from the Royal Children’s Hospital and Monash Health and endorsed at a monthly immunisation meeting. Attendees at this meeting include paediatricians, infectious disease physicians, nurse immunisation specialists, infection control team members and a representative from the Immunisation Section of the Victorian Department of Health.
These guidelines are based on the latest available evidence and aim to align with recommendations in the Sổ tay Chủng ngừa Úc.
tài trợ vắc xin
Một số khuyến nghị trong các hướng dẫn này nằm ngoài phạm vi của Chương trình Chủng ngừa Quốc gia (NIP). Các khu vực pháp lý khác nhau và từng bệnh viện có cách tiếp cận khác nhau đối với vắc xin không phải NIP, điều này cần được làm rõ với dịch vụ y tế địa phương.
We welcome any feedback on the guidelines, please email: [email protected]
Tài liệu
Các tác giả: Nigel Crawford (Director, SAEFVIC, Murdoch Children’s Research Institute) and Rachael McGuire (SAEFVIC Research Nurse, Murdoch Children’s Research Institute)
Đượcxem xét bởi: Rachael McGuire (MVEC Education Nurse Coordinator) and Annie Cobbledick (Immunisation Pharmacist, the Royal Children’s Hospital)
Ngày: tháng 3 năm 2021
Tài liệu trong phần này được cập nhật khi có thông tin mới và có vắc-xin. Nhân viên của Trung Tâm Giáo Dục Vắc-xin Melbourne (MVEC) thường xuyên xem xét độ chính xác của các tài liệu.
Quý vị không nên coi thông tin tại trang mạng này là lời khuyên y tế chuyên nghiệp, cụ thể cho sức khỏe của riêng mình hoặc sức khỏe riêng của gia đình quý vị. Đối với những mối lo ngại về y tế, bao gồm các quyết định về chủng ngừa, thuốc men và các phương pháp điều trị khác, quý vị phải luôn hỏi ý kiến chuyên gia y tế.